A step-by-step guide to the egg freezing process
Step 1: Basic “health” checks and screening tests
Although it is not a part of the egg freezing treatment, you will be tested for any infectious diseases, like HIV and hepatitis. This is to work out if your collected eggs need to be stored separately to prevent contamination of other egg samples. The UK regulatory body (known as the HFEA) requires fertility clinics to carry out these screening tests.
Several screening tests will be carried out to check if egg freezing is suitable for you. These may include an ultrasound scan and blood tests (e.g. AMH, FSH) to check hormone levels. Some of the test results will be used to decide the treatment approach by your specialist . Depending on the results, further tests may be required.

Step 2: Preparing ovaries for egg collection (“stimulation”)
Preparing the ovaries for egg collection involves daily injections with fertility drugs (containing hormones). These hormones stimulate your ovaries to produce multiple eggs, whereas in a natural cycle, only one egg would be produced by the ovaries.
Step 3: Monitoring
During the stimulation step, you will be carefully monitored, with ultrasound scans and blood tests, to check how your body is responding to the hormones.
Monitoring will not only make sure your ovaries are not over-stimulated but allows your specialist to spot the right moment for egg collection.

Step 4: Egg collection
A little before egg collection takes place (usually around 36 hours), you will receive a different hormone injection, to help with the release of the eggs.
Mature eggs are collected using a needle which is introduced into the vagina, or into the stomach. Ultrasound is used to carefully guide the needle into place. To make certain that you remain still during egg collection and that you do not feel any pain, you will be sedated, or under general anaesthetic.
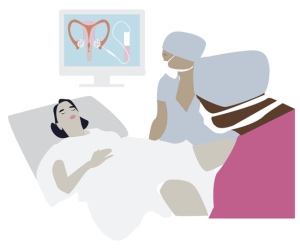
Step 5: Egg freezing
Before freezing, the eggs are treated with a solution which prevents ice crystals forming and damaging the egg during freezing; this solution is known as a cryoprotectant.
One of two methods will be used to freeze the eggs: a slow freeze process, or a new, fast-freezing, process known as vitrification.

Step 6: Egg storage
Frozen eggs are stored in their frozen state in tanks of liquid nitrogen, until they are needed.

Frequently Asked Questions
- How long does the egg freezing process take? It normally takes around 2 – 3 weeks from stimulation until the stage at which frozen eggs are stored.
- How many cycles do I need? It depends. Your specialist will advise you how many hormone stimulation cycles may be needed. This wil be based on your health, age and how your body responds to the drugs.
- How much does it cost? In the UK, the average cost of egg freezing (including scans, stimulations) is between £4,500 and £5,500 for one cycle. Storage costs are around £300 per year.

Connect with us